Easily absorbable calcium with vitamins D3, K1, and K2
- High-dosed and readily absorbed calcium supplement
- For the maintenance of bones
- The tablets are peppermint-flavored and can be chewed or swallowed whole
- Works well in combination with Bio-Magnesium
- Manufactured under Danish pharmaceutical control
BioActive Calcium+D3+K1+K2
| 1 tablet contains | % RDA* | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 500 mg | 63 % | |
| Vitamin D3 | 5 µg | 100 % | |
| Vitamin K | 35 µg | 47 % |
* RDA = Recommended Dietary Allowance.
Product Facts
Directions:
1 tablet daily, unless advised otherwise. The tablets can be chewed or swallowed whole. Preferably take before bedtime.
2 tablets per day for children up to 6 years of age, pregnant women, breastfeeding women, and people older than 60 years of age.
Do not exceed the recommended daily dosage.
Dietary supplements should not replace a varied diet.
A healthy lifestyle and a varied diet are important for maintaining good health.
Ingredients:
Calcium carbonate, sweetener: sorbitol, xylitol, anti-caking agent: polyvinyl-pyrrolidone, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, magnesium salts of fatty acids, flavor enhancer: peppermint powder, strenghtening agent: silicon dioxide, menaquinone (vitamin K2), phytomenadion (vitamin K1) and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3).
Storage:
Dark, dry, and at room temperature.
Keep out of reach of young children.
What is BioActive Calcium+D3+K1+K2?
BioActive Calcium+D3+K1+K2 contains vitamin D3 to increase the absorption of calcium in the body and vitamin K for good absorption of calcium in the bones.
BioActive Calcium+D3+K1+K2 is ideal in combination with BioActive Magnesium.
BioActive Calcium+D3+K1+K2 tablets contain nutrients that are important for the bones. The combination of calcium, vitamin D3, and vitamin K1/K2 helps maintain normal bone tissue. The calcium is ionized in the stomach, and the calcium ions are absorbed in the intestine with help from vitamin D3. Vitamin K is absorbed in the small intestine where it helps maintain healthy bones and supports blood coagulation. BioActive Calcium+D3+K1+K2 can also be chewed.
If you take two tablets per day, you can take them one at a time with separate meals.
What is Calcium?
Calcium is an element and also the most abundant mineral in the human body. The most prominent function of calcium is its role in maintaining normal teeth and bones. Bone tissue functions as the body's calcium storage facility. If the body gets too little calcium, it frees calcium from bone tissue to cover its needs.
- The amount of calcium that is not channeled into teeth and bones helps to support various body functions. Calcium contributes to:
- Normal maintenance of muscle function
- Normal nerve transmission
- Normal blood clotting
- Normal energy metabolism
- Normal functioning of digestive enzymes
Calcium and bones
Our bone mass is living tissue that is constantly being replaced. The bone-forming cells are called osteoblasts, while the bone-degrading cells are called osteoclasts. Because bone tissue also functions as the body's calcium storage facility it is importnt to absorb plenty of calcium in our bones. In situations where the body gets too little calcium from the diet, the osteoclasts are activated and break down bone tissue to release the calcium needed to cover the body's deficit.
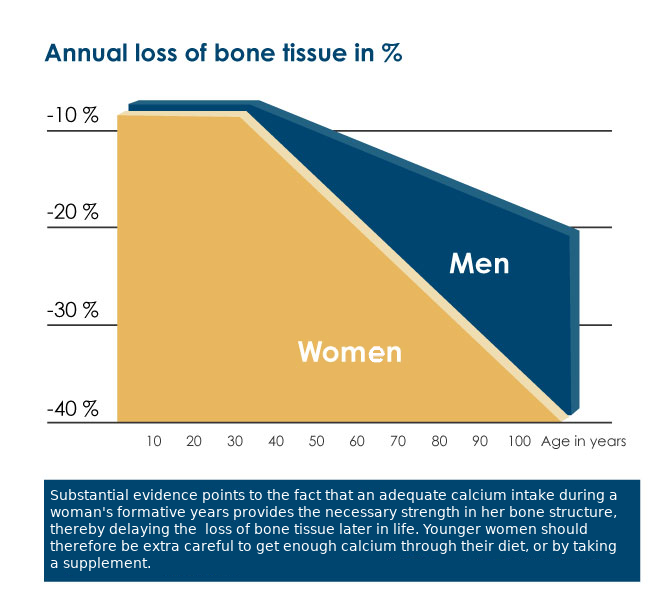
It is important to get plenty of calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin K during the years when your bones develop. Until the age of 30-35 years, our bone mass accumulates because the osteoblasts are more active than the osteoclasts. At some point, the two cell types reach a state of equilibrium. This is where our bone mass reaches its peak. The processes of establishing strongo and healthy bone mass is called “building a bone bank.” After reaching this point, the amount of calcium lost from the bones will exceed the amount that is stored. This causes a net loss of bone mass of around 0.6% per year. Although it is a slow and gradual loss, you will be better off if you have managed to build as much bone mass as possible from the beginning.
In addition to the age-related loss of bone, women are exposed to a hormone-related loss of bone mass starting at menopause. As a consequence, their total annual loss of bone mass can be as much as six per cent when their ovaries stop producing hormones.
Men generally only lose half as much bone mass as women do.
An active non-smoking lifestyle also helps to prevent loss of bone mass.
As shown in the following illustration, women are more exposed to loss of bone mass than men. Research shows that women who are treated with estrogen are not necessarily in less need of calcium.
Where do we get calcium?
- dairy products
- grain and seeds
- almonds
- nuts
- vegetables
- fruit
What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is available in several forms, of which D2 and D3 are the most important. D3 is the form of vitamin D that is absorbed most readily in the body. Vitamin D is actually a pro-vitamin because we are able to synthesize it in our skin when we get exposed to sufficient amounts of sunshine. However, at northern latitudes, we are only able to produce vitamin D from sunlight from May through September where the sun sits sufficiently high in the sky. Vitamin D helps the body metabolize calcium and is also needed for normal bones and muscle function.
Vitamin D:
- Has a role in the process of cell division and specialisation
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal bones,teeth and muscle function
- Plays a role in the absorption and utilization of calcium and phosphorus
- Contributes to normal blood calcium levels
- Supports a normal and well-functioning immune system
In recent years, science has focused on our need for vitamin D. Health authorities recommend
vitamin D supplements for children, pregnant women, dark-skinned children/adults, veiled women (and others who wear garments that cover most of the body), and for individuals who rarely or never
get exposed to sunlight. In addition, nursing home residents and people over the age of 70 are
advised to take vitamin D to help protect against brittle bones.
Calcium with vitamin D is necessary for normal bone formation in children.
What is vitamin K?
Vitamin K is a lipid-soluble vitamin that is needed for normal blood coagulation. It is also important for the maintenance of normal bone tissue, as it contributes the maintenance of normal bones by supporting the production of a bone-building protein called osteocalcin.
Vitamin K is found in two natural forms: K1 (phylloquinone) and K2 (menaquinone), and a variety of synthetic forms, including the water-soluble form called K3 (menadione). Vitamin K3 is not used in dietary supplements.
Vitamin K1 is found naturally in dark green vegetables. Vitamin K2 is produced by our intestinal bacteria. These bacteria can also transform K1 into different variants of K2. Infants can not form vitamin K. We usually get equal amounts of K1 and K2.
Vitamin K and medicine
People who take blood-thinning medication should beware that increased intake of vitamin K may reduce the effect of their medicine. However, the vitamin K doses that are known to neutralize the effect of blood-thinning drugs are 70-285 times higher than what is contained in a single tablet of BioActive Calcium+D3+K1+K2.
Official claims
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated the evidence behind calcium, Vitamin D and vitamin K and has acknowledged the following claims:
Calcium
- Is needed for the maintenance of normal bones and teeth
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal muscle function
- Contributes to normal blood clotting
- Contributes to normal neurotransmission
- Contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolism
- Contributes to normal function of digestive enzymes
- Has a role in the process of cell division and specialisation
- Calcium and vitamin D are needed for the normal growth and development of bone in children (Art. 14)
Vitamin D
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal bones and teeth
- Contributes to normal blood calcium levels
- Contributes to normal absorption/utilisation of calcium and phosphorus
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal muscle function
- Contributes to normal function of the immune system
- Has a role in the process of cell division and specialisation
- Vitamin D is needed for the normal growth and development of bone in children (Art. 14b)
Vitamin K
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal bones
- Contributes to normal blood clotting

